

















Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
The Need For High Speed Rail: Revolutionizing Transportation in the 21st Century

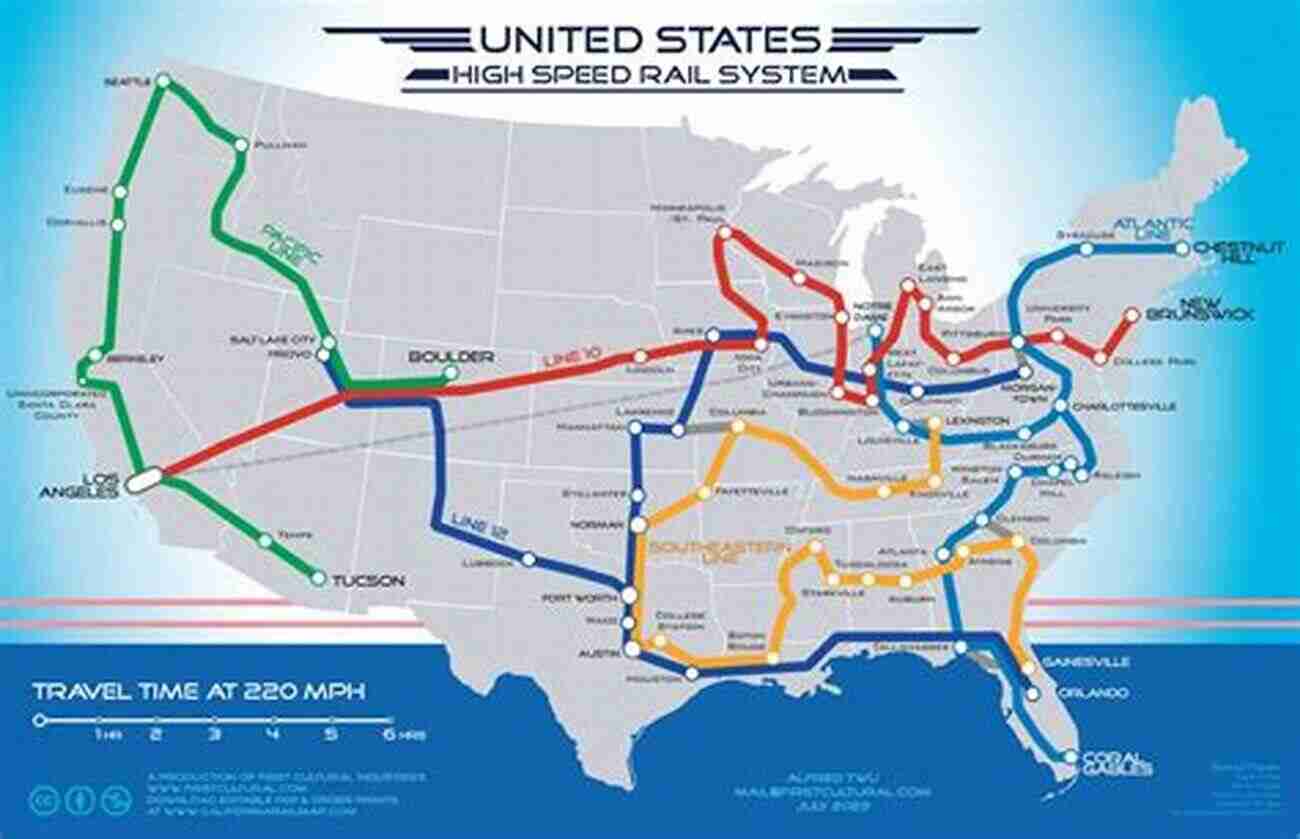
When it comes to transportation, speed is the name of the game. The world is moving at a rapid pace, and we need the means to keep up. That's where high-speed rail comes in. In this second edition, we delve deeper into the topic, exploring the vital need for high-speed rail in transforming the way we travel.
The High-Speed Revolution
Imagine being able to travel from one city to another in a matter of hours, free from congested highways and crowded airports. High-speed rail promises just that. With trains capable of reaching speeds of up to 300 miles per hour, the potential for revolutionizing transportation is enormous.
Connecting cities and communities like never before, high-speed rail offers a myriad of benefits. It enhances regional connectivity, facilitates efficient and reliable travel, reduces traffic congestion, and lowers greenhouse gas emissions. This mode of transportation also boosts economic growth by opening up new opportunities for businesses and attracting investment into previously underserved regions.
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 29878 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 523 pages |
| Lending | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
A Global Phenomenon
High-speed rail is not a new concept. Countries such as Japan, France, and China have already embraced this technology and reaped substantial rewards. Their interconnected networks have transformed domestic travel, making it faster, more convenient, and environmentally friendly. In fact, today, China boasts the world's largest high-speed rail network, with over 22,000 miles of track.
However, the need for high-speed rail extends far beyond these early adopters. As populations continue to soar, urban areas become more congested, and existing transportation infrastructure struggles to keep up with demand. Thus, many countries are now recognizing the urgent need to invest in high-speed rail to modernize their transportation systems and ensure sustainable growth.
Unlocking Economic Potential
One of the most compelling reasons to invest in high-speed rail is the economic benefits it brings. The construction and operation of such networks create jobs and stimulate economic activity. Additionally, high-speed rail connects regions, attracting businesses and tourism, and enabling commuters to access job opportunities in neighboring cities.
Furthermore, high-speed rail can bridge the gap between rural and urban areas, revitalizing isolated communities and achieving more balanced regional development. By reducing travel times, it becomes feasible for individuals to live in more affordable areas while still enjoying the opportunities and amenities of nearby urban centers.
Improving Transportation Efficiency
The need for high-speed rail in improving transportation efficiency cannot be underestimated. With road and air networks reaching capacity, finding sustainable alternatives becomes imperative. High-speed rail offers a viable solution, allowing for increased numbers of passengers to be moved swiftly and safely between destinations.
In addition, high-speed rail integrates seamlessly with existing transportation modes, providing efficient door-to-door journeys. Passengers can travel uninterrupted from city centers to city centers without the need for complicated transfers between airports or train stations.
Environmental Stewardship
In an era where climate change is at the forefront of global concerns, high-speed rail presents a greener alternative to traditional modes of transportation. Trains are more energy-efficient than cars or planes, emitting fewer pollutants and reducing carbon footprints. By shifting a significant portion of travelers away from these polluting forms of transport, high-speed rail plays a crucial role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
The Future of High-Speed Rail
The need for high-speed rail is not confined to a specific region or country; it is a global imperative. As technological advancements continue to enhance train speeds, safety, and sustainability, high-speed rail systems will become increasingly widespread and accessible.
With each new expansion or of high-speed rail, the benefits become more apparent. Communities are joined, economies flourish, and the world becomes a more connected place. It is ultimately an investment in progress, efficiency, and a sustainable future.
As the world rapidly evolves, so does our need for advanced transportation systems. High-speed rail offers a transformative solution that has unparalleled potential to reshape the way we travel. From economic growth to environmental stewardship, the benefits are undeniable.
It is time for governments, policymakers, and communities to embrace high-speed rail as the future of transportation. The second edition of 'The Need For High Speed Rail' reminds us of the urgency with which we must act. The time to invest in high-speed rail is now. Don't miss out on this revolution!
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 29878 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 523 pages |
| Lending | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
High-Speed Rail is seen as the single most viable competitor to the airline industry, as this ebook describes, in detail, the technology behind this emerging economic juggernaut. The material, unlike any ebook on this site, is rendered as 5 books in one, thus giving you a view of the industry from various perspectives:
1) HSR: History and Technology Précis (What is High-Speed Rail? Development of Motive Power for Railways Third Rail Systems Electrification Interfaces with Other Rail Elements Maglev Rail Station Location and Design: A Typology and Case Studies Tunnel Construction And Systems)
2. a) Impact of HSR Lecture #1 Topics (· ·Technological Evolution of the Present HST ·Main Models of HST ·Development of the HST Network ·Efficiency of High-speed Rail Systems ·What is the impact of High Speed Rail on tourism? ) b) Feasibility of HSR Lecture #2 Topics (· ·China’s high-speed rail system ·System performance ·Preconditions for new high-speed rail systems ·Economic feasibility of high-speed passenger rail systems in the United States ·s )
3. a) The Quest for Speed Documentary (Main subjects: Shrinking the nations, Crossing the Channel, British Rail, The European Rail Race, The New 'Golden Age' of rail, Magnetic sailing )
b) HSR Systems Around the World Article Topics ( Development of a total European network Improving the Russian Transport Infrastructure Asean and its relationship with China From Istanbul to Ankara The Indian corridors HSRs in other parts of the world Bridging the Gap Between Competing Land Use Issues with the California High-Speed Rail Project The popular argument stopping U.S. High-Speed Rail development Argument for HSR over Airline travel LCC effects in rail marketshare Modal shift The Brazilian railway market Summary)
Investing in high speed rail is a central planning decision. The government decides the of a new rail technology which allows trains running at a speed of 300-350 kilometres per hour (though the average commercial speed is substantially below the technically feasible speed). At the beginning of 2008 there were about 10,000 kilometers of new high speed lines in operation around the world and, in total (including upgraded conventional tracks),more than 20,000 kilometers of the worldwide rail network was devoted to provide high speed services.
The case for the HSR is strongly dependent on the volume of traffic where the new lines are built, the time savings and generated traffic and the average willingness to pay of passengers, the release of capacity in congested roads, airports or conventional rail lines and the reductions of external effects. The magnitude of the traffic volumes and shifts depends heavily on whether infrastructure costs are included in rail fares or financed by taxes. If rail infrastructure charges are based on short-run marginal cost, intermodal substitution will be dramatically affected by HSR public investment decisions. In this case ex ante cost-benefit analysis of HSR investment is, more than ever, a key element of transport policy.
George Haynes is the founder and CEO of the new startup company Logistic-Industrial Design Management and is a frequent contributor to LinkedIn.

 Anthony Burgess
Anthony BurgessEverything You Need To Know About Building Referral...
Are you looking for ways to boost revenue...

 Aleksandr Pushkin
Aleksandr PushkinThe Fascinating History of Afro Uruguay - Unveiling the...
Afro Uruguay refers to the rich and diverse...

 Anton Foster
Anton FosterReflections From Stubborn Son: A Journey of...
Have you ever encountered a stubborn...

 Brennan Blair
Brennan BlairDiscover the Revolutionary World of Protein Modelling:...
Protein modelling is an essential...

 Ricky Bell
Ricky BellThe Best Old Fashioned Advice: Timeless Wisdom Passed...
Have you ever turned to your grandparents,...

 Isaiah Price
Isaiah PriceEmbark on an Unforgettable Journey: The Sword and Sorcery...
Are you ready to be...

 Hassan Cox
Hassan CoxThe Enchanting World of Wendy Darling Comes Alive in...
Step into the magical world of Neverland...

 Ivan Turner
Ivan TurnerAdsorption Calculations And Modelling Chi Tien: Unlocking...
In the field of chemistry, adsorption is a...

 Harvey Hughes
Harvey HughesUnleashing the Full Potential of a Team: How To Organize...
"Genius is 1% inspiration and 99%...

 Desmond Foster
Desmond FosterThe Fascinating Journey of George Romanes: From...
George John Romanes, born on May 20, 1848,...

 Adrien Blair
Adrien BlairThe Untold Truth: The Bible In The Early Church - A...
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur...
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!

 Ezekiel CoxThe Decline Of The WWF In 1995 Titan Trilogy: A Tale of Lost Glory, Betrayal,...
Ezekiel CoxThe Decline Of The WWF In 1995 Titan Trilogy: A Tale of Lost Glory, Betrayal,...
 Dan HendersonPractical Reptile Keeping August 2014 - A Comprehensive Guide for Reptile...
Dan HendersonPractical Reptile Keeping August 2014 - A Comprehensive Guide for Reptile...
 Winston HayesThe Ultimate Guide to Improving Reading Comprehension: 10-30 Exercises by...
Winston HayesThe Ultimate Guide to Improving Reading Comprehension: 10-30 Exercises by... Brennan BlairFollow ·15.9k
Brennan BlairFollow ·15.9k Gene SimmonsFollow ·8.5k
Gene SimmonsFollow ·8.5k Neil GaimanFollow ·11.8k
Neil GaimanFollow ·11.8k Daniel KnightFollow ·3k
Daniel KnightFollow ·3k Junot DíazFollow ·18.4k
Junot DíazFollow ·18.4k Jace MitchellFollow ·15.2k
Jace MitchellFollow ·15.2k Bruce SnyderFollow ·4.2k
Bruce SnyderFollow ·4.2k Ryan FosterFollow ·18.8k
Ryan FosterFollow ·18.8k

















