

















Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
The Empirical Theory of Light: Shedding Light on Empirical Theories

Have you ever wondered about the nature of light? How does it travel from its source and enable us to see the world around us? The study of light has fascinated scientists and philosophers for centuries, leading to the development of various empirical theories. In this article, we will explore the empirical theory of light and delve into its history, principles, and applications in the modern world. So, get ready to illuminate your mind with the wonders of the empirical theory of light!
A Brief History of the Empirical Theory of Light
The concept of light has been a subject of speculation and inquiry since ancient times. Ancient Greek philosophers, such as Empedocles and Democritus, proposed various theories about the nature of light. However, it was in the 17th century that empirical observations and experiments paved the way for a more comprehensive understanding of light.
Renowned scientists like Isaac Newton and Christian Huygens developed competing theories known as the corpuscular theory and the wave theory, respectively. Newton's corpuscular theory suggested that light consists of tiny particles emitted from a source, while Huygens' wave theory proposed that light travels in the form of waves.
4.3 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 2925 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Word Wise | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 50 pages |
| Paperback | : | 390 pages |
| Item Weight | : | 1.34 pounds |
| Dimensions | : | 6.14 x 0.88 x 9.21 inches |
These two theories sparked numerous debates and experiments among scientists, leading to the eventual formulation of the empirical theory of light that we know today.
Principles of the Empirical Theory of Light
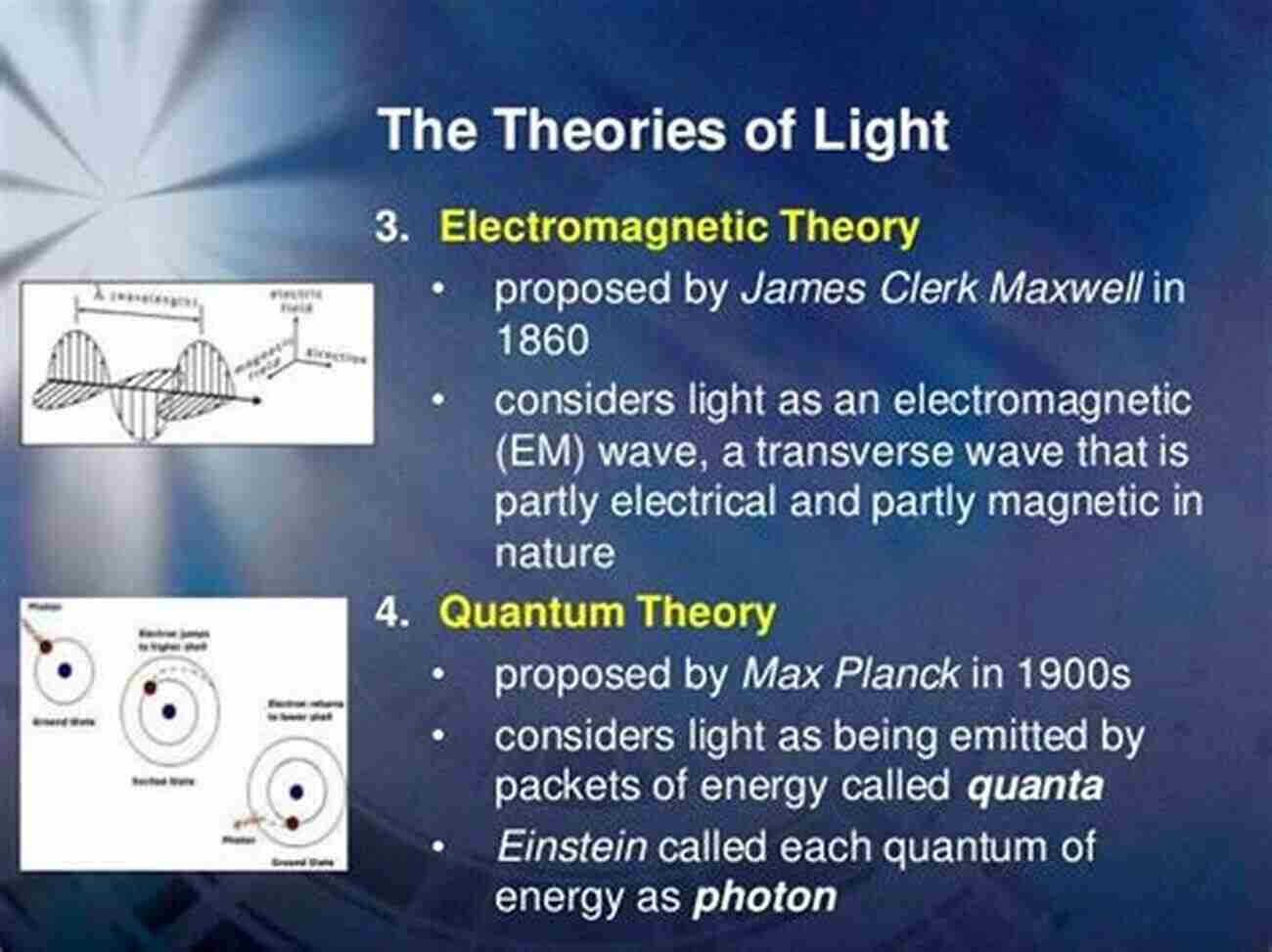
The empirical theory of light is based on the principle that light behaves as both particles and waves, depending on the context and observed phenomena. This principle, known as wave-particle duality, is a cornerstone of modern physics.
According to this theory, light is made up of tiny particles called photons. Photons possess both energy and momentum, and they travel in straight lines unless their path is altered by obstacles or the presence of a medium.
Additionally, the empirical theory of light acknowledges the wave-like properties of light. When light encounters an obstacle or a narrow opening, it diffracts and creates interference patterns. These patterns are a clear indication of its wavelike nature.
Furthermore, the empirical theory also explains the phenomenon of reflection and refraction, which are crucial aspects of light's behavior. When light strikes a surface, it can bounce off (reflection) or change direction as it passes through a different medium (refraction). These phenomena have countless practical applications in fields like optics and telecommunications.
Applications and Significance of the Empirical Theory of Light
The empirical theory of light has paved the way for various technological advancements and practical applications in our daily lives. Here are some of the ways this theory has revolutionized different fields:
- Optics: The empirical theory of light is fundamental to optics, the branch of physics that deals with the behavior and properties of light. It has led to the creation of devices like telescopes, microscopes, and cameras, enabling us to explore the vastness of the universe and examine objects at the microscopic level.
- Telecommunications: Fiber optics, a technology extensively used in modern telecommunications, relies on the principles of the empirical theory of light. It allows for the transmission of data through thin strands of glass or plastic fibers, revolutionizing the way we communicate.
- Quantum Mechanics: The empirical theory of light plays a crucial role in the field of quantum mechanics, which deals with the behavior of matter and energy at the smallest scales. It provides insights into phenomena like quantum entanglement and the dual nature of particles.
- Medical Imaging: The principles of the empirical theory of light enable various medical imaging techniques like X-rays, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI),and ultrasound. These techniques help in diagnosing and treating a wide range of medical conditions.
The empirical theory of light has significantly shaped our understanding of the nature and behavior of light. Through its principles, we have gained insights into the dual nature of light, its ability to propagate as waves, and its existence as particles called photons. This theory has not only deepened our knowledge of the physical world but has also led to groundbreaking technological advancements in various fields. As we continue to explore the mysteries of light, the empirical theory remains a guiding light in our quest for knowledge.
So the next time you switch on a light bulb or marvel at a beautiful rainbow, remember the remarkable journey of the empirical theory of light and its impact on our lives.
4.3 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 2925 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Word Wise | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 50 pages |
| Paperback | : | 390 pages |
| Item Weight | : | 1.34 pounds |
| Dimensions | : | 6.14 x 0.88 x 9.21 inches |
If we assume that atom are transparent then all matter would be transparent; which is not true. If we assume that atoms’ are translucent then all matter would be translucent; which again is not true either. If you assume that atoms’ are however opaque and have reflective surfaces and acknowledge pores exist between the atoms of a molecule caused by the shape of atoms; then we can attribute a body’s ability or inability to let light through as a result of the way the atoms of the body are arranged.
Number of Words: 7883
Number of A4 Sized Pages: 26
This is an article; not a book.
Audience: General public

 Anthony Burgess
Anthony BurgessEverything You Need To Know About Building Referral...
Are you looking for ways to boost revenue...

 Aleksandr Pushkin
Aleksandr PushkinThe Fascinating History of Afro Uruguay - Unveiling the...
Afro Uruguay refers to the rich and diverse...

 Anton Foster
Anton FosterReflections From Stubborn Son: A Journey of...
Have you ever encountered a stubborn...

 Brennan Blair
Brennan BlairDiscover the Revolutionary World of Protein Modelling:...
Protein modelling is an essential...

 Ricky Bell
Ricky BellThe Best Old Fashioned Advice: Timeless Wisdom Passed...
Have you ever turned to your grandparents,...

 Isaiah Price
Isaiah PriceEmbark on an Unforgettable Journey: The Sword and Sorcery...
Are you ready to be...

 Hassan Cox
Hassan CoxThe Enchanting World of Wendy Darling Comes Alive in...
Step into the magical world of Neverland...

 Ivan Turner
Ivan TurnerAdsorption Calculations And Modelling Chi Tien: Unlocking...
In the field of chemistry, adsorption is a...

 Harvey Hughes
Harvey HughesUnleashing the Full Potential of a Team: How To Organize...
"Genius is 1% inspiration and 99%...

 Desmond Foster
Desmond FosterThe Fascinating Journey of George Romanes: From...
George John Romanes, born on May 20, 1848,...

 Adrien Blair
Adrien BlairThe Untold Truth: The Bible In The Early Church - A...
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur...
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!

 David PetersonExperience Virginia's Legendary Santa Trains with Donna Strother Deekens - A...
David PetersonExperience Virginia's Legendary Santa Trains with Donna Strother Deekens - A...
 Mario BenedettiAre You Ready for a Lifelong Friendship? Find Out Everything You Need To Know...
Mario BenedettiAre You Ready for a Lifelong Friendship? Find Out Everything You Need To Know...
 Peter CarterThe Fascinating World of Chemoinformatics: Theory, Practice, and Innovative...
Peter CarterThe Fascinating World of Chemoinformatics: Theory, Practice, and Innovative...
 Elliott CarterHarnessing Images Instagram Infographics And Pinterest To Grow Your Business
Elliott CarterHarnessing Images Instagram Infographics And Pinterest To Grow Your Business Desmond FosterFollow ·11.5k
Desmond FosterFollow ·11.5k Christopher WoodsFollow ·6k
Christopher WoodsFollow ·6k Dalton FosterFollow ·3.2k
Dalton FosterFollow ·3.2k Jules VerneFollow ·9.6k
Jules VerneFollow ·9.6k David Foster WallaceFollow ·16.4k
David Foster WallaceFollow ·16.4k Aleksandr PushkinFollow ·16.8k
Aleksandr PushkinFollow ·16.8k Jedidiah HayesFollow ·19.4k
Jedidiah HayesFollow ·19.4k Samuel BeckettFollow ·7.4k
Samuel BeckettFollow ·7.4k
















