















Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
The Impact of Darwinian Evolution on Social Policy and Social Theory Series

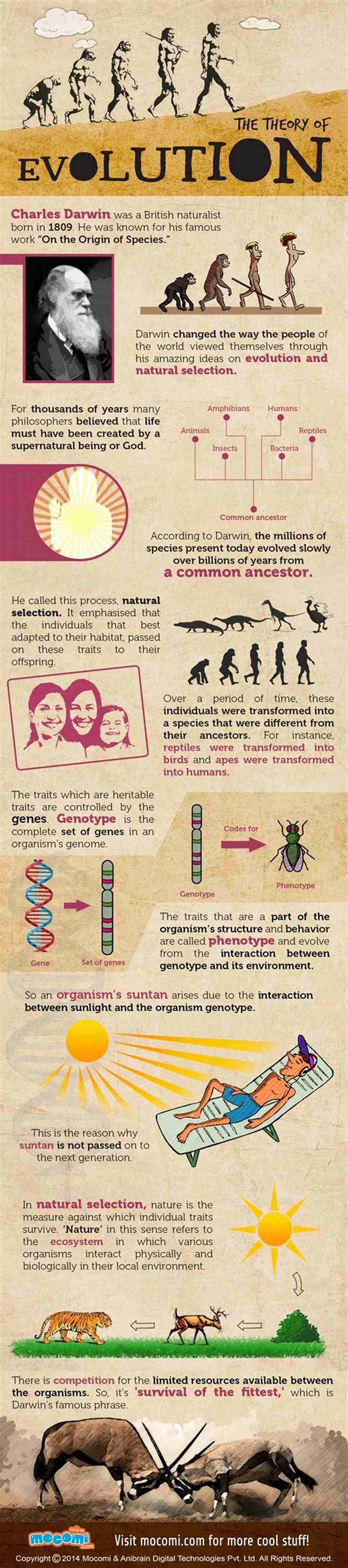
When Charles Darwin introduced his theory of evolution by natural selection, it revolutionized the scientific world. However, his groundbreaking research didn't only have implications for biology and genetics. Darwinian evolution is closely tied to social policy and social theory as well. In this article, we will explore the impact of Darwinian evolution on social policy and social theory and how it has shaped our understanding of human societies.
The Basics of Darwinian Evolution
Before delving into its societal implications, let's briefly recap the basics of Darwinian evolution. Darwin proposed that species gradually evolve through the process of natural selection. Variations within a population exist, and those individuals with traits better suited to their environment have a higher chance of survival and reproduction. Over time, these advantageous traits become more prevalent in the population.
Now, let's dive into the relationship between Darwinian evolution, social policy, and social theory.
4.1 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 554 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Word Wise | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 149 pages |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
Impact on Social Policy
Darwin's theory challenged traditional views on the nature of humanity and the role of society in shaping individuals. It provided a scientific framework for understanding the origins and development of humans, which had significant implications for social policy.
One key impact of Darwinian evolution on social policy was the concept of "survival of the fittest." This notion suggested that individuals who were more biologically fit would be more successful in society. It influenced policies and ideologies such as eugenics, which aimed to improve the genetic quality of the population by controlling reproduction. This had profound consequences, particularly during the early 20th century when eugenics was used to justify forced sterilization and discrimination.
Furthermore, Darwinian evolution highlighted the importance of adaptation and competition within societies. This idea shaped social policies related to economic systems, as it favored laissez-faire capitalism and meritocracy. The notion that individuals should be rewarded according to their abilities and efforts reflected the principles of natural selection.
Integration with Social Theory
Darwinian evolution also influenced various social theories, providing new perspectives on human behavior, cultural development, and societal structures.
Sociobiology, a field that emerged in the 20th century, uses the principles of Darwinian evolution to explain social behavior. It suggests that certain behaviors and social structures have evolved due to their adaptive advantages. For example, altruistic behavior can be understood as a form of kin selection, where individuals are more likely to help their relatives who share their genetic material.
Darwinian evolution also contributed to the development of evolutionary psychology, a field exploring the psychological adaptations that have evolved in humans. It proposes that human behavior, emotions, and cognition have been shaped by natural selection, providing insights into topics such as mate selection, aggression, and parental care.
Contemporary Debates
While Darwinian evolution has had a significant impact on social policy and social theory, it remains a topic of debate and controversy.
One ongoing discussion revolves around the potential misinterpretation of evolutionary principles, leading to social Darwinism and justifications for inequality or discrimination. Critics argue that biological determinism overlooks the complexity of human behavior and culture, and that social policies should be based on principles of fairness, equality, and justice, rather than on notions of biological superiority.
Another debate centers around the balance between nature and nurture. While Darwinian evolution emphasizes the role of genetics and biological factors, social theorists argue that cultural and environmental influences shape human behavior to a significant extent. Understanding and addressing the interplay between nature and nurture remains a challenge for policymakers and social theorists alike.
The impact of Darwinian evolution on social policy and social theory cannot be underestimated. It challenged traditional views, influenced policies like eugenics, and provided new perspectives on human behavior and societal structures. However, it also sparked debates around the potential misinterpretation of evolutionary principles and the balance between nature and nurture. As our understanding of evolution continues to evolve, it is crucial to critically examine its implications for society and ensure that social policies are based on ethical principles that prioritize equality and justice.
example.com
4.1 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 554 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Word Wise | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 149 pages |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
In little more than a hundred years the evolutionary theory of Charles Darwin has conquered the thinking world. No other body of ideas has enjoyed such unrivaled success. But precisely because of its scientific status, Darwinism has sometimes been invoked to sustain other ideas and beliefs with a much less solid foundation. Darwinian Evolution is a study of the historical background of Darwin's ideas, of their logical structure, and of their alleged and actual implications.
Flew explores the Scottish Enlightenment, an important and often neglected aspect of Darwin's intellectual background. He compares Darwin with such figures as Adam Smith, Thomas Malthus, and Karl Marx, emphasizing not the similarities, but the differences between the natural and social sciences. Flew argues that social science must do what natural science does not: take account of individual choice. He examines the creationist controversy in Britain and the United States and discusses the possibility of a human sociobiology.
In his new , Flew updates his book by discussing relevant works that have appeared since it was published thirteen years ago. He discusses two different tendencies among both social scientists and those who develop or promote social policies according to various findings in the social sciences: (1) to assume there is no such thing as human nature; and (2) to take no account of the possibility that differences between sets of individuals may be genetically determined. Flew maintains that both these tendencies violate Darwin's theory. Darwinian Evolution is an intriguing study that should be read by sociologists, biologists, philosophers, and all those interested in the impact of Darwin and his work.

 Anthony Burgess
Anthony BurgessEverything You Need To Know About Building Referral...
Are you looking for ways to boost revenue...

 Aleksandr Pushkin
Aleksandr PushkinThe Fascinating History of Afro Uruguay - Unveiling the...
Afro Uruguay refers to the rich and diverse...

 Anton Foster
Anton FosterReflections From Stubborn Son: A Journey of...
Have you ever encountered a stubborn...

 Brennan Blair
Brennan BlairDiscover the Revolutionary World of Protein Modelling:...
Protein modelling is an essential...

 Ricky Bell
Ricky BellThe Best Old Fashioned Advice: Timeless Wisdom Passed...
Have you ever turned to your grandparents,...

 Isaiah Price
Isaiah PriceEmbark on an Unforgettable Journey: The Sword and Sorcery...
Are you ready to be...

 Hassan Cox
Hassan CoxThe Enchanting World of Wendy Darling Comes Alive in...
Step into the magical world of Neverland...

 Ivan Turner
Ivan TurnerAdsorption Calculations And Modelling Chi Tien: Unlocking...
In the field of chemistry, adsorption is a...

 Harvey Hughes
Harvey HughesUnleashing the Full Potential of a Team: How To Organize...
"Genius is 1% inspiration and 99%...

 Desmond Foster
Desmond FosterThe Fascinating Journey of George Romanes: From...
George John Romanes, born on May 20, 1848,...

 Adrien Blair
Adrien BlairThe Untold Truth: The Bible In The Early Church - A...
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur...
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!

 Thomas PynchonQuantum Legacies Dispatches From An Uncertain World: Unlocking the Secrets of...
Thomas PynchonQuantum Legacies Dispatches From An Uncertain World: Unlocking the Secrets of...
 Ian PowellThe Laboratory Mouse Handbook Of Experimental Animals - A Comprehensive Guide...
Ian PowellThe Laboratory Mouse Handbook Of Experimental Animals - A Comprehensive Guide... Ira CoxFollow ·3.8k
Ira CoxFollow ·3.8k Tom ClancyFollow ·11.4k
Tom ClancyFollow ·11.4k Ernest J. GainesFollow ·14.4k
Ernest J. GainesFollow ·14.4k Jackson BlairFollow ·7k
Jackson BlairFollow ·7k Ivan TurgenevFollow ·11k
Ivan TurgenevFollow ·11k Preston SimmonsFollow ·11.6k
Preston SimmonsFollow ·11.6k William PowellFollow ·5.8k
William PowellFollow ·5.8k Jermaine PowellFollow ·8.2k
Jermaine PowellFollow ·8.2k